Building a web app with Noir and Barretenberg
NoirJS is a Typescript package meant to work both in a browser and a server environment.
In this tutorial, we will combine NoirJS with Aztec's Barretenberg backend to build a simple web app. From here, you should get an idea on how to proceed with your own Noir projects!
You can find the complete app code for this guide here.
Dependencies
Before we start, we want to make sure we have Node installed. If you don't have it already you can install it here, we recommend using Yarn as our package manager for this tutorial.
We'll also need version 1.0.0-beta.15 nargo installed, see the Noir installation guide for details.
Let's go barebones. Doing the bare minimum is not only simple, but also allows you to easily adapt it to almost any frontend framework.
Barebones means we can immediately start with the dependencies even on an empty folder 😈:
yarn add @noir-lang/noir_js@1.0.0-beta.15 @aztec/bb.js@3.0.0-nightly.20251104 buffer vite vite-plugin-node-polyfills@0.17.0
Wait, what are these dependencies?
noir_jsis the main Noir package. It will execute our program, and generate the witness that will be sent to the backend.bb.jsis the Typescript interface for Aztec's Barretenberg proving backend. It also uses thewasmversion in order to run on the browser.
In this guide, we will install versions pinned to 1.0.0-beta.15. These work with Barretenberg version 3.0.0-nightly.20251104, so we are using that one version too. Feel free to try with older or later versions, though!
Setting up our Noir program
ZK is a powerful technology. An app that reveals computational correctness but doesn't reveal some of its inputs is almost unbelievable, yet Noir makes it as easy as a single line of code.
It's not just you. We also enjoy syntax highlighting. Check out the Language Server
All you need is a main.nr and a Nargo.toml file. You can follow the noirup installation and just run noirup -v 1.0.0-beta.15, or just create them by hand:
mkdir -p circuit/src
touch circuit/src/main.nr circuit/Nargo.toml
To make our program interesting, let's give it a real use-case scenario: Bob wants to prove he is older than 18, without disclosing his age. Open main.nr and write:
fn main(age: u8) {
assert(age > 18);
}
This program accepts a private input called age, and simply proves this number is higher than 18. But to run this code, we need to give the compiler a Nargo.toml with at least a name and a type:
[package]
name = "circuit"
type = "bin"
This is all that we need to get started with Noir.

Compile compile compile
Finally we're up for something cool. But before we can execute a Noir program, we need to compile it into ACIR: an abstract representation.
This can be done by cd-ing into our circuit directory and running the nargo compile command.
cd circuit
nargo compile
This will write the compiled circuit into the target directory, which we'll then load into our JS later on.
Setting up our app
Remember when apps only had one html and one js file? Well, that's enough for Noir webapps. Let's create them in the project root:
touch index.html index.js
And add something useful to our HTML file:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<head>
<style>
.outer {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
width: 100%;
}
.inner {
width: 45%;
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 10px;
word-wrap: break-word;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<script type="module" src="/index.js"></script>
<h1>Noir app</h1>
<div class="input-area">
<input id="age" type="number" placeholder="Enter age" />
<button id="submit">Submit Age</button>
</div>
<div class="outer">
<div id="logs" class="inner"><h2>Logs</h2></div>
<div id="results" class="inner"><h2>Proof</h2></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
It could be a beautiful UI... Depending on which universe you live in. In any case, we're using some scary CSS to make two boxes that will show cool things on the screen.
As for the JS, real madmen could just console.log everything, but let's say we want to see things happening (the true initial purpose of JS... right?). Here's some boilerplate for that. Just paste it in index.js:
const show = (id, content) => {
const container = document.getElementById(id);
container.appendChild(document.createTextNode(content));
container.appendChild(document.createElement('br'));
};
document.getElementById('submit').addEventListener('click', async () => {
try {
// code will go in here
} catch {
show('logs', 'Oh 💔');
}
});
At this point in the tutorial, your folder structure should look like this:
.
├── circuit
│ ├── Nargo.toml
│ ├── src
│ │ └── main.nr
│ └── target
│ └── circuit.json
├── index.html
├── index.js
├── package.json
├── etc...
Some more JS
We're starting with the good stuff now. We want to execute our circuit to get the witness, and then feed that witness to Barretenberg. Luckily, both packages are quite easy to work with. Let's import them at the top of the file and initialize the WASM modules:
import { Barretenberg, UltraHonkBackend } from '@aztec/bb.js';
import { Noir } from '@noir-lang/noir_js';
import initNoirC from '@noir-lang/noirc_abi';
import initACVM from '@noir-lang/acvm_js';
import acvm from '@noir-lang/acvm_js/web/acvm_js_bg.wasm?url';
import noirc from '@noir-lang/noirc_abi/web/noirc_abi_wasm_bg.wasm?url';
import circuit from './target/circuit.json';
// Initialize WASM modules
await Promise.all([initACVM(fetch(acvm)), initNoirC(fetch(noirc))]);
And instantiate them inside our try-catch block:
const noir = new Noir(circuit);
const barretenbergAPI = await Barretenberg.new();
const backend = new UltraHonkBackend(circuit.bytecode, barretenbergAPI);
Executing and proving
Now for the app itself. We're capturing whatever is in the input when people press the submit button. Inside our try block, let's just grab that input and get its value. Noir will gladly execute it, and give us a witness:
const age = document.getElementById('age').value;
show('logs', 'Generating witness... ⏳');
const { witness } = await noir.execute({ age });
show('logs', 'Generated witness... ✅');
For the remainder of the tutorial, everything will be happening inside the try block
Now we're ready to prove stuff! Let's feed some inputs to our circuit and calculate the proof:
show('logs', 'Generating proof... ⏳');
const proof = await backend.generateProof(witness);
show('logs', 'Generated proof... ✅');
show('results', proof.proof);
Our program is technically done . You're probably eager to see stuff happening! To serve this in a convenient way, we can use a bundler like vite by creating a vite.config.js file:
touch vite.config.js
Noir needs to load two WASM modules, but Vite doesn't include them by default in the bundle. We need to add the configuration below to vite.config.js to make it work.
We also need to target ESNext since bb.js uses top-level await, which isn't supported in some browsers.
import { defineConfig } from 'vite';
import { nodePolyfills } from 'vite-plugin-node-polyfills';
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [
nodePolyfills({
// Whether to polyfill specific globals.
globals: {
Buffer: true,
global: true,
process: true,
},
// Whether to polyfill `node:` protocol imports.
protocolImports: true,
}),
],
optimizeDeps: {
exclude: ['@aztec/bb.js'],
},
resolve: {
alias: {
pino: 'pino/browser.js',
},
},
});
This should be enough for vite. We don't even need to install it, just run:
yarn vite dev
If it doesn't open a browser for you, just visit localhost:5173. You should now see the worst UI ever, with an ugly input.
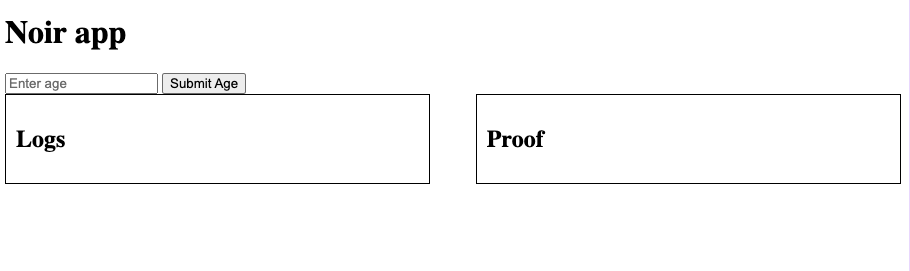
Now, our circuit requires a private input fn main(age: u8), and fails if it is less than 18. Let's see if it works. Submit any number above 18 (as long as it fits in 8 bits) and you should get a valid proof. Otherwise the proof won't even generate correctly.
By the way, if you're human, you shouldn't be able to understand anything on the "proof" box. That's OK. We like you, human ❤️.
Verifying
Time to celebrate, yes! But we shouldn't trust machines so blindly. Let's add these lines to see our proof being verified:
show('logs', 'Verifying proof... ⌛');
const isValid = await backend.verifyProof(proof);
show('logs', `Proof is ${isValid ? 'valid' : 'invalid'}... ✅`);
You have successfully generated a client-side Noir web app!

Next steps
At this point, you have a working ZK app that works on the browser. Actually, it works on a mobile phone too!
If you want to continue learning by doing, here are some challenges for you:
- Install nargo and write Noir tests
- Change the circuit to accept a public input as the cutoff age. It could be different depending on the purpose, for example!
- Enjoy Noir's Rust-like syntax and write a struct
Countrythat implements a traitMinAgewith a methodget_min_age. Then, make a structPersonhave anu8as its age and a country of typeCountry. You can pass apersonin JS just like a JSON objectperson: { age, country: { min_age: 18 }}
The world is your stage, just have fun with ZK! You can see how noirjs is used in some common frameworks in the awesome-noir repo.